A Fourier Disparity Layer representation for Light Fields
31st May 2019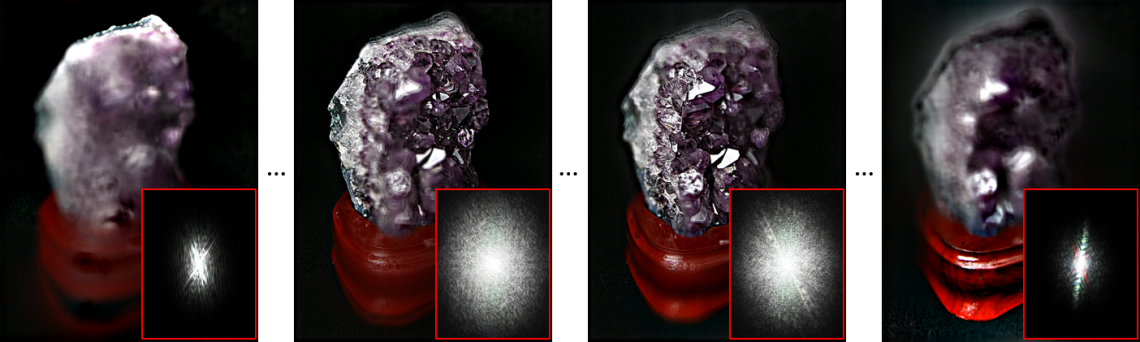
Principle
The Fourier Disparity Layer (FDL) model, is a representation of Light Fields allowing efficient processing by fully exploiting the parallelisation capabilities of modern GPUs.
In the FDL representation, the scene is decomposed into a set of additive layers and each layer of index k is associated to a disparity value dk representing its depth. Any view of the light field at angular coordinate (u,v) is directly reconstructed as the sum of the layers shifted with a translation vector (u.dk, v.dk).
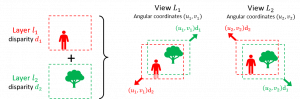
The construction of layers from light field views is performed efficiently in the Fourier Domain thanks to a linear least squares optimisation problem formulated independently for each frequency component (efficiently solved with parallel processing on a GPU). This is made possible by the fact that in the Fourier domain, the shifting operation simply consists in multiplying each frequency component by a complex weight, hence resulting in a linear relationship between views and layers.
Publications
- The paper [1], presents the theoretical foundations of the model and various applications including calibration of angular coordintates and disparity values, view interpolation, denoising, real-time rendering (see demo video below).
- Extensions of the FDL construction for light field super-resolution, demosaicing and completion applications are presented in [2]. By performing completion jointly with super-resolution and demosaicing, the method also allows the extraction of high quality views from RAW lenslet data of plenoptic cameras (see examples of results below).
- The compression of light fields is addressed in [3] with a view prediction scheme based on the FDL view interpolation.
- Another light field compression and streaming method that directly encodes the FDL model is presented in [4]. It constructs a binary tree structure from the layers to encode the FDL in a hierarchical manner, thus providing a scalable representation for light field streaming.
[2] M. Le Pendu and A. Smolic “High Resolution Light Field Recovery with Fourier Disparity Layer Completion, Demosaicing, and Super-Resolution”, IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP) Apr. 2020. (watch the talk here)
Code
The matlab code is available on github: here!
Results
| Demonstration of the applications in [1] |
|---|
| Examples of view extraction from lenslet RAW data of a Lytro Illum camera [2] (click on images for full resolution) | |
|---|---|
| FDL Extraction | Lytro Desktop (official Lytro software) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |





